×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Honda Parts
- Honda Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
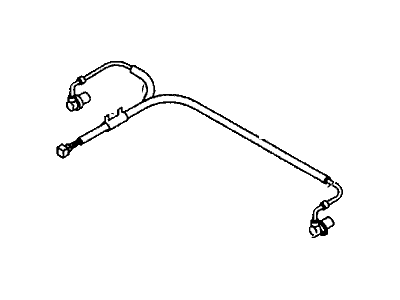
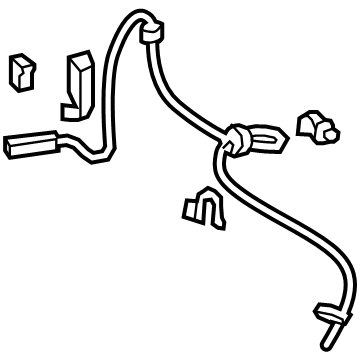
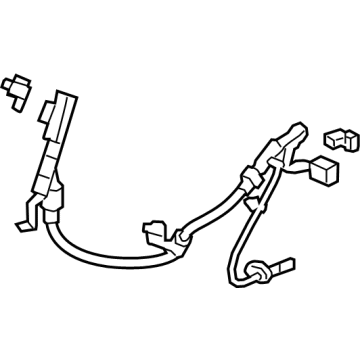
Genuine Honda Passport Speed Sensor
Speed Control Sensor- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
20 Speed Sensors found
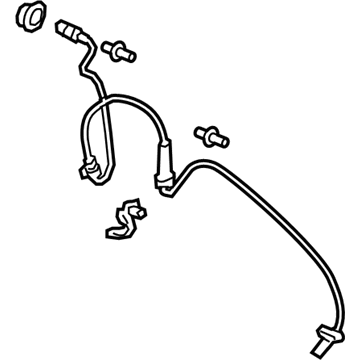
Honda Passport Sensor Assembly, Right Front
Part Number: 57450-TZ5-A02$35.49 MSRP: $50.13You Save: $14.64 (30%)
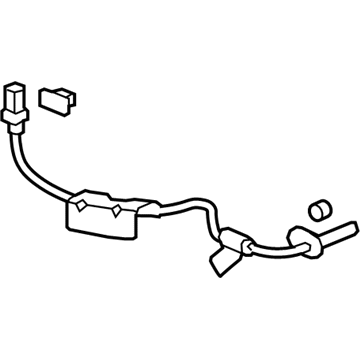
Honda Passport Sensor Assembly, Right Rear
Part Number: 57470-TZ6-A02$35.67 MSRP: $50.38You Save: $14.71 (30%)
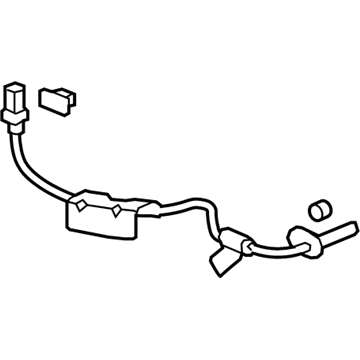
Honda Passport Sensor Assembly, Left Rear
Part Number: 57475-TZ5-A02$35.35 MSRP: $49.93You Save: $14.58 (30%)
Honda Passport Sensor Assembly, Right Rear
Part Number: 57470-TZ5-A02$35.35 MSRP: $49.93You Save: $14.58 (30%)
Honda Passport Sensor Assembly, Left Rear
Part Number: 57475-TZ6-A02$35.67 MSRP: $50.38You Save: $14.71 (30%)
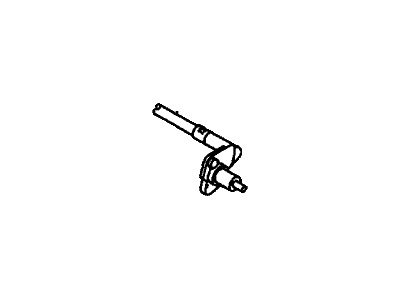
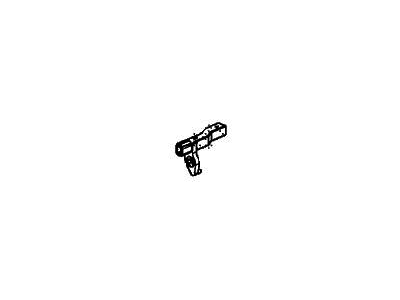
Honda Passport Sensor, Right Front Wheel Speed
Part Number: 8-97256-535-1$338.66 MSRP: $554.92You Save: $216.26 (39%)
Honda Passport Sensor, Right Front Speed
Part Number: 8-97125-316-2$80.98 MSRP: $189.57You Save: $108.59 (58%)Honda Passport Sensor Assembly, Left Front
Part Number: 57455-TZ5-A02$36.08 MSRP: $50.97You Save: $14.89 (30%)Honda Passport Sensor, Rear Speed Wheel
Part Number: 8-97118-810-0$49.05 MSRP: $200.95You Save: $151.90 (76%)Honda Passport Sensor, Rear Wheel Speed Anti-Lock Brake
Part Number: 8-97096-409-1$32.62 MSRP: $267.23You Save: $234.61 (88%)Honda Passport Sensor, Left Front Wheel Speed
Part Number: 8-97256-536-1$203.20 MSRP: $554.92You Save: $351.72 (64%)
Honda Passport Speed Sensor
The function of the Speed Sensor in Honda Passport is to monitor the speed and rotation of the wheels with the help of data that is conveyed to computer modules in the car to change the functions of the engine and the anti-lock brake system. These include VSS and WSS systems that use ferromagnetic toothed reluctor rings and passive as well as active sensors. Speed sensors also find use in rail vehicle applications with the two most prominent technologies being Hall effect and magnetoresistive sensing technologies which are enable optimal performance of the unit in harsh environments. There has been development of better sensing technologies resulting to better signals and outcomes, new developmental designs such as motor encoders and bearing less sensors has made speed measurement in the different applications to be more precise.
In search of affordable OEM Honda Passport Speed Sensor? Consider browsing through our extensive inventory of genuine Honda Passport Speed Sensor. Not only do we provide market-leading prices and a manufacturer's warranty, but we also pride ourselves on exceptional customer service and swift delivery.
Honda Passport Speed Sensor Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: Where is the Vehicle Speed Sensor Located on Honda Passport?A:The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) is located on the transfer case for 4WD models or on the transmission for 2WD models. It produces a pulsing voltage signal that is translated by the PCM into miles-per-hour, which is used to operate the cruise control system, the speedometer, and the torque converter clutch and shift solenoid in the transmission. A defective VSS can cause various driveability and transmission problems. On O8D-I vehicles, the VSS is a permanent magnet generator triggered by a toothed rotor on the transmission output shaft. On OBD-11vehicles, the VSS is a hall-effect switch. To check the VSS, raise the vehicle and support it securely on jackstands. Locate the VSS and unplug the electrical connector from it. Inspect the connector terminals and the VSS wire harness for any damage. On OBD-I vehicles, use a digital voltmeter to back-probe the two wire terminals of the VSS connector. The sensor should produce a minimum of 0.5 volts and the voltage should increase as the transmission output shaft rotates faster. If the VSS is defective, replace it. Testing the VSS on OBD-II vehicles is beyond the scope of the home mechanic. To replace the VSS, raise the vehicle and support it securely on jackstands. Disconnect the electrical connector from the VSS. Remove the hold-down bolt and the hold-down clamp and pull the VSS out of the transfer case or transmission. Whether you're installing the old VSS or a new unit, be sure to replace the O-rings. Tighten the hold down bolt to the torque. Installation is otherwise the reverse of removal.
Related Honda Passport Parts
Browse by Year
2026 Speed Sensor 2025 Speed Sensor 2024 Speed Sensor 2023 Speed Sensor 2022 Speed Sensor 2021 Speed Sensor 2020 Speed Sensor 2019 Speed Sensor 2002 Speed Sensor 2001 Speed Sensor 2000 Speed Sensor 1999 Speed Sensor 1998 Speed Sensor 1997 Speed Sensor 1996 Speed Sensor 1995 Speed Sensor 1994 Speed Sensor